
Special Issue on Canadian Perspectives on Information Science
Guest Editor: Brian Detlor
May 2025

Introduction to the Special Issue on Canadian Perspectives on Information Science
As a means of showcasing the unique approaches, values, and topics of special interest held by Canadian information scientists to the global community at large, this special issue – hosted by the Association of Information Science and Technology’s (ASIS&T) Canada Chapter – showcases Canadian perspectives on Information Science research and practice.

Information and You: McGill’s Perspectives on Human-Information Interaction Research
From cybersecurity to archives, and everything in between, research at the McGill University School of Information Studies centers around human-information interaction (HII) – putting people, their experiences, their needs, and their priorities at the heart of the research. These vignettes highlight some of the research from SIS faculty, and how it connects people with the information that matters to them.

Colonial Tensions: Reconciling Intellectual Freedom and Indigenous Knowledge Systems in One Canadian iSchool
How do we further the enormous task of truth and reconciliation between the fundamental principle of intellectual freedom with the collective sovereignty due to our First Nations siblings? This is a recurring question and theme of the course Foundations of Intellectual Freedom in Librarianship at the iSchool of the University of British Columbia. In the winter of 2023, I was tasked with the development of a dedicated course on intellectual freedom. It is currently one of only three such courses in Canada, alongside the University of Alberta and the University of Toronto.

The Great Canadian Breakdown: What will it take to get a “Right to Repair” in Canada?
Fixing things in Canada has never been more difficult. Smartphones, laptops, refrigerators, washing machines, smart speakers, virtual assistants, cars, bicycles, wheelchairs, pacemakers, ventilators, tractors, tanks, fighter jets, and almost every other device or piece of equipment in our homes and workplaces is more costly, more inconvenient, and more difficult, if not impossible, to repair. Barriers to repair impact all industries, sectors, and regions. No one is spared from the Great Canadian Breakdown. As breakdown becomes more pervasive, the need for a comprehensive Canadian “right to repair” becomes more critical.

Information in Times of Crisis: Learning Together
During the summer of 2020, we offered a new graduate course, “Information in Times of Crisis.” With growing recognition of the ways pressing issues such as climate change impacts, racial injustice, and health crises are intertwined, we wanted to better prepare library and information studies graduates to navigate these crises, while experiencing the Covid-19 pandemic together.

Forging a Middle Path: Canada’s Moment to Lead in AI Governance
Today, with the AI landscape evolving rapidly, especially with the explosive advancement of generative AI technologies, Canada finds itself pulled between two global powers: the United States, favouring open innovation, and the European Union, doubling down on strict AI regulation. Canada does have a proposed Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA), introduced in 2022 as part of Bill C-27, which aims to regulate high-impact AI systems. However, AIDA is still under review and has yet to be finalized, leaving a critical gap in national legislation.
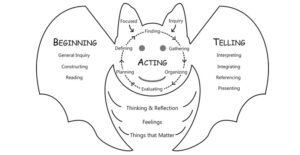
Stepping Up to BAT: Inspiration for a Research Process Model
Wouldn’t it be great that at the same time you were learning to read chapter books and basic informational texts, you could learn a research process that could carry you right through post-secondary studies? As M. E. Marland, a member of the UK Schools Council, asserted in 1981, from elementary school to PhD studies, in research, the questions and processes remain fundamentally the same. To find out if that was true for the Canadian context, for my PhD dissertation study I decided to observe the information behaviours of grade-three students as they worked on a class project.

Western Alumni Leading the Discipline
This article gives a short overview of the impact Western PhD graduates have had and continue to have on ASIS&T and on the discipline.

Setting the Course and Embracing the Journey: Reflections on Knowledge Mobilization in the Canadian Research Context
Knowledge mobilization (KMb) is the movement of research findings between and within academic and non-academic settings. In a recent SSHRC-funded partner development project, Supporting Transparent and Open Research Engagement and Exchange (STOREE), we constructed a KMb plan as part of our funding application. Our work focused on making research more accessible, relevant to, and useful for non-academic audiences, and supporting scholars to change practices around research sharing. Reflecting on the project, team composition, how we worked together, sub-project processes and outcomes, and individual learnings, we gained insights on making alternative outputs and KMb more broadly.

Health Information Without Borders: The Struggles and Strategies of Older Chinese Adults in Canada
Have you ever struggled to find the right health information, unsure of where to turn or what advice to trust? For many older Chinese adults in Canada, this challenge is even greater. They often face situations such as navigating a complex healthcare system, overcoming language barriers, and balancing traditional health beliefs with Western medical practices. These challenges can impact how they make health decisions and their overall well-being. Through in-depth interviews with 20 older Chinese adults in Canada, our research explores various factors related to how they seek and use health information. What did we uncover? Join us as we delve into their stories and the broader implications for health equity in Canada.

Studying Exploratory Search in Public Digital Libraries: Collaboration & Partnerships
Most search interfaces currently used in public digital libraries have been influenced by design patterns based on web search, even though the complexity of the information seeking process when searching within a public library can be far greater than web search. Web search interfaces work extremely well for lookup search tasks, but they struggle to support complex search, especially those related to exploratory search.

Building Capacity for Decision Making Where Information Matters
As educators, we believe we have a responsibility to equip students entering professional careers with the knowledge and skills to consider evidence critically, to understand the roles of various actors who could and should be included in decision processes, and how to arrive at solutions to societal problems effectively. Accordingly, for over a decade we have offered a graduate course, Information in Public Policy and Decision Making, in the Dalhousie University Master of Information program. Unique among the Canadian Information Studies programs, this course is designed to introduce students to the many facets of evidence-based (or evidence-informed) policy and decision-making with the expectation that as the next generation professionals they will understand when and how to facilitate policy development at organizational and local, national, and international levels.

Digital Self-Determination: Data Sovereignty in Inuvialuit Communities of Canada’s Western Arctic
Since 2013, researchers from the University of Alberta School of Library and Information Studies and the Inuvialuit elders, leaders, and community members in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region (ISR), Northwest Territories have collaborated to develop digital library and digital storytelling platforms to support Inuvialuit cultural heritage digitization, revitalization, preservation and access.

Naloxone Now! Canadian Librarians Save Lives
Nearly 50% of library workers in Canada have responded to an opioid overdose at work, while only half of library workers who had responded to a suspected overdose on the job felt that they had been properly trained or were confident in how they handled the situation. This situation should give us pause: most library workers are unequipped to handle this very real part of the job. As iSchool educators, we ought to ask ourselves: what are we going to do about this? Can saving lives be considered a core LIS principle?

Tracing “CanCon” in Library and Information Science Research
LIS professionals and practitioners may find it challenging to access current research that supports library decision-making, program development, or service evaluation through a distinctly Canadian lens. Public, school, and special libraries did not seem to have the same kind of representation in the research, and it made me wonder: what is the state of Canadian LIS research content?

Toward Sustainable Data Governance in Refugee and Immigrant Serving Sector in Canada
For governments across the world, evaluating the impact of social service programs is a growing challenge – and they are increasingly turning to data and technology to help manage it. This is especially true for programs serving refugees and immigrants to settle in a new country. From tracking who needs settlement support to deciding who gets benefits first, digital systems and artificial intelligence (AI) are becoming key tools in how social services support refugees and immigrants. But what happens when data systems try to capture something as human and complex as “support”?

A Canadian Approach to Rethinking Technology Design for Aging Populations
Older adults are the fastest-growing segment of the population. In Canada, one in five people are 65 or older, and by 2065, this will increase to more than one in four. Yet, despite their growing numbers, older adults often face exclusion and marginalization in technology design. This digital divide has significant consequences, leading to isolation, loneliness, frustration, and poor health outcomes, particularly when we intersect factors like lower socioeconomic status, race, gender, and immigrant status.

Information Literacy Instruction in Canadian Libraries
Longitudinal research in information science is rare, but an exception to that rule is a Canadian study that has surveyed academic librarians at multiple points over a 30-year period to understand their instructional goals and practices. This research program highlights the value of longitudinal and geographic comparisons.

Multilingual Scholarly Communication and Translation Technologies
While a multilingual scholarly communication ecosystem would help to mitigate many of the inequities created by the single-language model that currently prevails, multilingualism nonetheless presents its own challenges. If researchers all publish in their own language, how will they be able to discover and access each other’s work? Can new AI-based translation technologies help?




