How do mobile health apps empower users to enhance well-being during pandemics?
How Do Mobile Health Apps Empower Users To Enhance Well-Being During Pandemics?
Zhongyun Zhou, Xiao-Ling Jin, Carol Hsu, and Zhenya Tang
The COVID-19 pandemic has triggered enormous challenges in healthcare (e.g., limited access to physical hospital services), thus threatening public well-being. These challenges are prevalent globally and especially salient in developing countries with insufficient and unevenly distributed healthcare resources. To tackle these challenges, people have adopted mobile health (mHealth for short) apps on a large scale. By providing health-related services to users via mobile devices and applications, mHealth apps are expected to play an important role in improving users’ well-being during the pandemic.
—mHealth apps enabled users to autonomously and effectively achieve their health managing purpose, thus leading to a sense of empowerment—
In this research, we aimed to understand how mHealth apps empower end-users to enhance their well-being against the pandemic event. We defined the psychological empowerment of mHealth users (PEMU) as users’ sense of being able to manage their health autonomously and effectively through the use of mHealth apps. On this basis, we developed a research model to examine how PEMU influences users’ subjective well-being under external events and how technological features of mHealth apps affect PEMU (see Figure 1). Then we tested the model through a mixed-methods investigation containing two studies: (1) a quantitative study with 602 Chinese mHealth users during COVID-19, and (2) a follow-up qualitative study of 326 online articles and reviews.
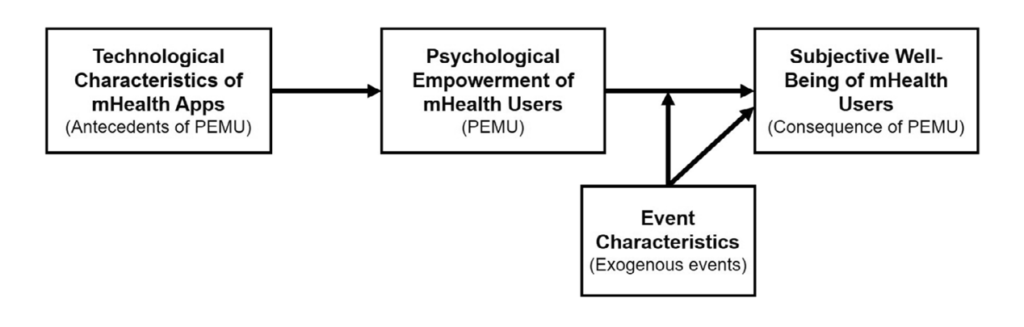
So, what did we find? First and foremost, PEMU improved users’ subjective well-being in two ways: (1) PEMU enhanced users’ vitality. This vitality-stimulating effect was more salient when users perceived the pandemic event to be more critical. (2) PEMU reduced users’ stress. Users felt stressed when they perceived the pandemic event to be critical and disruptive. PEMU showed a stress-buffering effect and, thus, improved users’ well-being. Both vitality-stimulating and stress-buffering effects are important, especially for less healthy users who usually feel less vitality and more stress.
Last but not least, we found that PEMU appeared when users perceived mHealth apps to be useful for tackling pandemic-caused challenges for healthcare, easy to use, and of high quality. In this case, mHealth apps enabled users to autonomously and effectively achieve their health managing purpose, thus leading to a sense of empowerment.
In one sentence, our work found that PEMU, driven by three technological characteristics (perceived effectiveness, user-friendliness, and quality), enhanced users’ well-being during COVID-19 through both (1) a stress-buffering effect, which counterbalanced the detrimental, stress-increasing effects of event criticality and disruption, and (2) a vitality-stimulating effect, which was intensified by event criticality.

Our research findings provide useful insights to healthcare providers, public administrators, and mHealth developers regarding the design and application of mHealth. For example, policymakers could leverage mHealth to empower people to establish resilience against severe external shocks like the COVID-19 pandemic. Further, mHealth app developers could improve the empowering role of their product by focusing on the effectiveness, user-friendliness, and quality of app design in terms of information, system, and services.
Undoubtedly, more efforts are needed to push the research into a broader field in terms of time, region, and ICT tools. We urge future researchers to do so.
For the details of this research, please see:
Zhou, Z., Jin, X.-L., Hsu, C., & Tang, Z. (2022). User empowerment and well-being with mHealth apps during pandemics: A mix-methods investigation in China. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.24695
Cite this article in APA as: Zhou, Z., Jin, X.-L., Hsu, C., & Tang, Z. (2022, August 17). How do mobile health apps empower users to enhance well-being during pandemics? Information Matters, Vol. 2, Issue 8. https://informationmatters.org/2022/08/how-do-mobile-health-apps-empower-users-to-enhance-well-being-during-pandemics/
Author
-
Zhongyun (Phil) Zhou is an Associate Professor in the School of Economics and Management at Tongji University and Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning. He holds two Ph.D. degrees from University of Science and Technology of China and City University of Hong Kong. His current research interest focuses on the usage and impacts of emerging digital technologies (e.g., social media, mobile technologies, artificial intelligence, blockchain, data analytics, and the Metaverse) for sustainable development. His papers appear in renowned journals such as Journal of Management Information Systems, Journal of Business Ethics, European Journal of Information Systems, Information & Management, Decision Support Systems, Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, and others. He serves on the editorial board for such journals as Information Systems Journal (Associate Editor and Guest Co-Editor for a special issue), Information Technology and People (Senior Editor), and Electronic Commerce Research and Applications (Associate Editor). He has received numerous awards including the Chinese Information Economy Society’s Youth Innovation Award and International Consortium for E-Business’s Best Paper Award.
View all posts





