A Rumor Reversal Model of Online Health Information during the Covid-19 Epidemic
A Rumor Reversal Model of Online Health Information during the Covid-19 Epidemic
Xiwei Wang
Rumor during the Covid-19 epidemic
The Covid-19 epidemic has profoundly changed the global economy and society, bringing all individuals and organizations into the VUCA era—an era of Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity. The development of the Internet and social media has expanded the speed and scope of information dissemination. Is the information about the new crown pneumonia circulating in social media true and credible? Wouldn’t these rumors have a negative impact on netizens and social stability? Especially during the global Covid-19 epidemic, thus the lack of health-related knowledge among Internet users, the massive increase in demand for health information stimulates the dissemination of health information by mass media. It also provides opportunities for rumor-mongers to publish and spread online rumors of health information. If the online rumors related to inaccurate health information cannot be disinformed and controlled in time, it is very easy to trigger social panic, which affects social public order and also destabilizes society under crisis events. Reversing and controlling the spread of online rumors about health information is an important social issue for online rumor management and public opinion guidance during the current Covid-19 epidemic.
—Reversing and controlling the spread of online rumors about health information is an important social issue for online rumor management and public opinion guidance during the current Covid-19 epidemic.—
Our study examined the following research questions: (1) how to construct the G-SCNDR network rumor reversal model based on the traditional infectious disease SIR model, combined with the theory of scientific knowledge level; (2) to determine the spreading scale and reversal path of the G-SCNDR network rumor reversal model, taking the “Shuanghuanglian incident” network rumor during the new crown pneumonia as an example; (3) the sensitivity analysis of the parameters of the G-SCNDR network rumor reversal model was conducted to determine countermeasures and to improve the efficiency of the network rumor reversal model.
Simulation of rumor propagation and reversal

Based on the comprehensive consideration of internal and external factors of health information network rumor propagation and reversal, the scientific knowledge level theory was adopted to classify the types of users in social networks. We selected the specific strategies of health information network rumor propagation, constructed the network rumor reversal model G-SCNDR, and conduct a global simulation of the process of health information network rumor propagation and reversal for comparative analysis.
The G-SCNDR model of online rumor reversal
The G-SCNDR model of online rumor reversal is based on the traditional SIR model of infectious diseases and adopts the scientific knowledge level theory and the “isolation-transformation” strategy. According to the model, the rumor reversal process is divided into two phases, including the information vacuum phase (phase 1, Figure 1) and the information disclosure phase (phase 2, Figure 2). The vacuum phase refers to the phrase before the official node adopts external control strategies and the information disclosure phase after the adoption of external control strategies. In the information vacuum phase, health information network rumors spread on social media. Under the influence of scientific knowledge level, susceptible users in the system will be transformed into three states, respectively, users who deny network rumors after being exposed to them, users C(t) who believe network rumors and spread them, and users U(t) who are unable to determine the truthfulness of network rumors to remain neutral and may spread them.
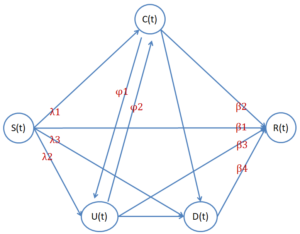
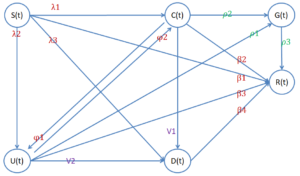
At a certain point t0, the official agency implements the external intervention “isolation-transformation” strategy. The official agency finds some influential gullible nodes and neutral nodes that spread online rumors, artificially converts these users into users of disinformation and retweets the disinformation tweets to prove the authority and authenticity of the published disinformation, and names such people as government spokesperson nodes G(t).
At this point in the system, neutral nodes and gullible nodes spontaneously start to convert into denial nodes due to the appearance of disinformation with authority. At the same time, due to the presence of government spokesman nodes, two ways of conversion of gullible nodes into denial nodes appear. Figure 1 shows the state transformation of users in the process of online rumor propagation, and Figure 2 shows the transformation of users’ state in the process of online rumor reversal.
“Isolation-transformation” strategy
From the perspective of internal and external factors, the study adopts the scientific knowledge level theory and external network rumor control strategy based on the SIR model, constructs the G-SCNDR network rumor reversal model, simulates the proposed G-SCNDR model using the simulation analysis method, and conducts sensitivity analysis on important parameters of the model, and proposes that the “isolation-transformation” strategy can better control online rumors. It is found that by appropriately adopting the “isolation-conversion” strategy as a measure for external control of online rumors, improving the penetration rate of users’ scientific knowledge, and promoting the conversion efficiency of official nodes, the reversal efficiency of the G-SCNDR online rumor reversal model can be improved. The study can help to better understand the spread of online rumors and the process of online rumor reversal in the context of public health emergencies and provide some guidance and reference for online rumor control during public health emergencies.
The source of the paper
Wang, X., Li, Y., Li, J., Liu, Y., & Qiu, C. (2021). A rumor reversal model of online health information during the Covid-19 epidemic. Information Processing and Management, 58(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2021.102731
Cite this article in APA as: Wang, X. (2022, May 27). A rumor reversal model of online health information during the Covid-19 epidemic. Information Matters, Vol. 2, Issue 5. https://informationmatters.org/2022/05/a-rumor-reversal-model-of-online-health-information-during-the-covid-19-epidemic/





